Mastering Your Taxes: A Beginner's Guide to Easy Income Tax Filing in South Africa
Welcome to our beginner's guide to income tax filing in South Africa. In this blog post, we will provide a clear and simplified overview of South African income tax, who needs to pay it, and why it's important to submit your annual income tax return. We'll also explore some tax deductions that you can claim back. Let's dive in!
1. What is South African income tax, and how does it differ from UIF?
South African income tax is a tax imposed by the South African Revenue Service (SARS) on individuals who earn taxable income above a certain threshold. It is important to note that income tax and the Unemployment Insurance Fund (UIF) are separate obligations.
Income tax is applicable to various sources of income, such as salaries, wages, bonuses, commissions, rental income, investment gains, and more. The tax rates and calculations for income tax differ depending on the type of taxpayer.
· Salary Earners: Individuals who earn a salary as their primary source of income are typically considered salary earners. The income tax for salary earners is calculated based on a progressive tax system with different tax brackets. As your income increases, the applicable tax rate increases gradually.
· Provisional Tax Payers: Provisional taxpayers include self-employed individuals, freelancers, and individuals earning income from business activities. They are required to estimate their taxable income and make payments in advance, usually twice a year. Provisional tax payments help individuals meet their tax obligations throughout the year and avoid a large tax liability at year-end.
2. Who must pay this income tax?
The requirement to pay income tax in South Africa depends on various factors, including income level, filing status, and age. Here are some general guidelines:
a. Tax Thresholds: For the tax year 2022/2023 (subject to change), the income tax thresholds are as follows:
· Individuals below 65 years: No income tax payable if the annual taxable income is below R87,300.
· Individuals between 65 and 75 years: No income tax payable if the annual taxable income is below R135,150.
· Individuals 75 years and older: No income tax payable if the annual taxable income is below R151,100.
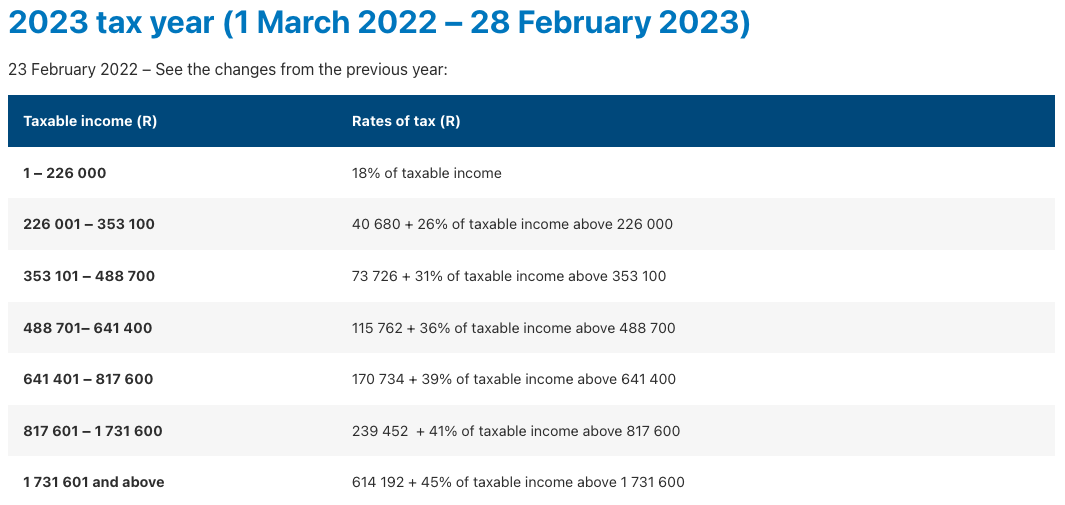
b. Income Tax Brackets: South Africa uses a progressive tax system with different tax brackets and rates. Here is an example income tax table (subject to change) for individuals below 65 years:
Individual tax tables for 2023 tax year
Source SARS website
3. Why is it important to submit your annual income tax return?
Submitting your annual income tax return is crucial for several reasons:
· Compliance: It ensures that you meet your legal obligations as a taxpayer and avoid penalties or legal issues.
· Claiming Refunds: If you've paid more tax than you owe through monthly PAYE deductions or provisional tax payments, filing your return allows you to claim a refund.
· Tax Planning: Filing your return provides an opportunity to review your financial situation, assess any tax-saving opportunities, and optimize your tax position for the upcoming year.
Income Tax Filing Dates in South Africa:
It's important to be aware of the specific income tax filing dates in South Africa. While these dates can change each year, here are the general timelines:
Non-provisional taxpayers: The 2023 tax filing season opens on 07 July 2023 at 8 pm and closes on 23 October 2023. During this period, non-provisional taxpayers can submit their income tax returns for the previous tax year.
Provisional taxpayers: Provisional taxpayers, who are required to make advance tax payments during the tax year, have different deadlines. The first provisional tax payment is due by the end of August, and the second payment is due by the end of February of the following year. The final income tax return must be submitted by the relevant tax season deadline of 24 January 2024.
4. What are some tax deductions that you can claim back?
South African tax law allows for various deductions that can help reduce your taxable income. To claim deductions, you need to substantiate your claims with appropriate documentation. Here are some common tax deductions:
· Medical Expenses: You may claim a portion of qualifying medical expenses not covered by medical aid. Keep receipts, invoices, and medical certificates as proof.
· Retirement Contributions: Contributions to registered retirement funds, such as pension or provident funds, are deductible within certain limits. Keep documentation from your fund or financial institution.
· Donations: Donations made to approved public benefit organizations may be tax-deductible. Ensure you have a valid receipt or certificate from the organization.
· Home Office Expenses: If you work from home, you may claim a portion of your expenses, such as rent, utilities, and internet costs. Keep records of your expenses and supporting documents.
Conclusion
Understanding South African income tax is essential for every taxpayer. By knowing who needs to pay, the tax thresholds, and the importance of filing your annual income tax return, you can navigate the process more confidently. Additionally, being aware of tax deductions available to you allows for potential savings. Remember to consult with a tax professional or refer to SARS guidelines for specific advice based on your circumstances.
We hope this beginner's guide has provided you with a clearer understanding of South African income tax. If you have any further questions, feel free to reach out to our team at DigMe Solutions.